Bhutan

Continent – Asia
Region – Southern Asia
Size – 47,000 km²
Geography – Mostly mountainous with some savanna and fertile valleys
Language – Dzongkha, Tibetan and Nepalese dialects
Religion – 75% Buddhist, 28% Hindu
Monetary Unit – Ngultrum
Natural Resources – timber, gypsum, calcium carbonate
Agriculture – rice, corn, root crops, citrus, foodgrains; dairy products, eggs
Industry – cement, wood products, processed fruits, alcoholic beverages, calcium carbide, tourism
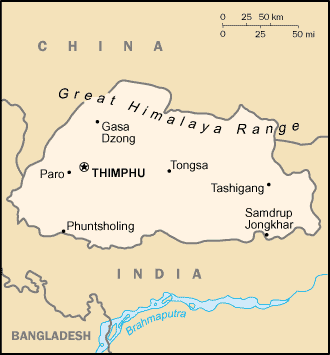
Neighbouring Countries – China, India
Population – 733,643 (2014)
Population Growth Rate – 2.08%
Average Life Expectancy – 55.1
Capital City – Thimphu (population 79,185)
Highest Mountain – Kula Kangri (7,553 m)
Longest River – Manas (Gongri) (3,200 km )
Climate – Cool winters 2°C to 19°C and hot summers 20°C to 30°C in valleys, cold winters and cool summers in mountains with year round snow
Yearly Rainfall – 140 cm approx mostly during May to October Monsoon season
Plant Life – rhododendron, juniper, magnolia, carnivorous plants, rare orchids, blue poppy (the national flower), edelweiss, gentian, medicinal plants, daphne, giant rhubarb, high-altitude plants, tropical trees, pine and oak
Animal Life – golden langur, red panda, snow leopard, takin, musk deer, Himalayan brown bear, Himalayan marten, tiger, mountain goat and timid blue sheep
Bird Life – black-necked crane, pheasant, hornbill
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Bhutan. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Facts_Figures/Country_Facts/bhutan.htm. Last accessed Monday, July 18, 2016
Facts and Figures Pages
