Burma (Myanmar)

Continent – Asia
Region – South-east Asia
Size – 678,500 km²
Geography – Central lowlands surrounded by highlands
Language – Burmese
Religion – 89% Buddhist, 4% Christian, 4% Islam, 3% other
Monetary Unit – Kyat
Natural Resources – petroleum, timber, tin, antimony, zinc, copper, tungsten, lead, coal, some marble, limestone, precious stones, natural gas
Agriculture – rice, pulses, beans, sesame, groundnuts, sugarcane; hardwood; fish and fish products
Industry – agricultural processing; wood and wood products; copper, tin, tungsten, iron; cement, construction materials; pharmaceuticals; fertilizer; natural gas; garments, jade and gems
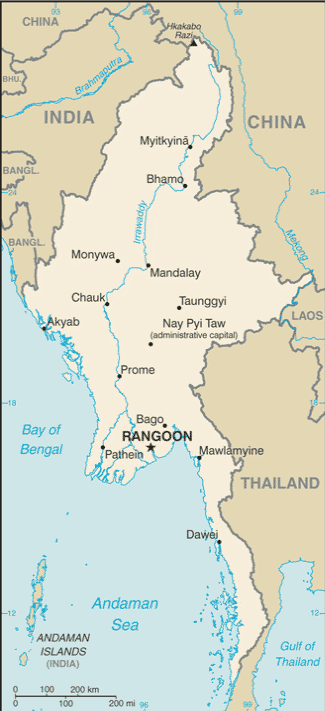
Neighbouring Countries – India, China, Laos, Thailand
Population – 55,746,253 (2014 estimate)
Population Growth Rate – 0.81%
Average Life Expectancy – 62.49
Capital City – Nay Pyi Taw (1,558,367)
Largest City – Yangon (formerly Rangoon) (population 5,209,541)
Highest Mountain – Hkakabo Razi (5,881 m)
Longest River – Ayeyarwady (2,170 m)
Climate – Monsoon – hot, humid, cloudy, wet summers – 24°C to 36°C, mild, dry winters – 18°C to 30°C
Yearly Rainfall – 320 cm (approx)
Plant Life – evergreen forest, teak, bamboo, palm, mangrove, swamp plants, scrub vegetation
Animal Life – monkeys, tigers, leopards, elephants, wild dogs
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Burma (Myanmar). Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Facts_Figures/Country_Facts/burma_myanmar.htm. Last accessed Monday, July 18, 2016
Facts and Figures Pages
