North America
Geography
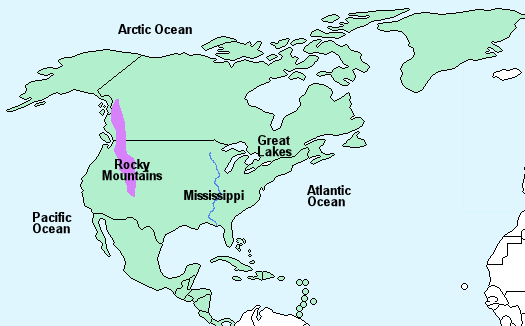
North America is the World’s third-largest continent – 24,474,000 km² covering approximately 16.5% of the Earth’s land and 5% of the Earth’s surface.
It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
The eastern side of the continent is generally lower than the west which contains the Rocky mountains. The five Great Lakes lie on the United States Canadian border.
The highest mountain is Mt McKinley in Alaska (6,194 m) and the longest river is the Mississippi (3,765 km).
Regions & Seasons
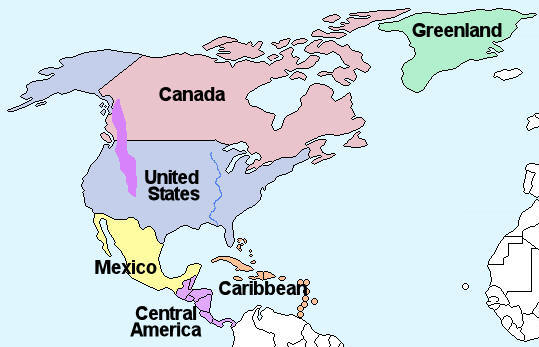 North America can be broadly divided into the six regions shown on the map (right).
North America can be broadly divided into the six regions shown on the map (right).
Greenland, Canada and most of the United States lie in the Northern hemisphere and have four distinct seasons
– Spring – March, April, May
– Summer – June, July, August
– Autumn – September, October, November
– Winter – December, January, February
Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and southern United States have more constant temperatures throughout the year but have a wet season – May to October and a dry season – November to April.
Climate
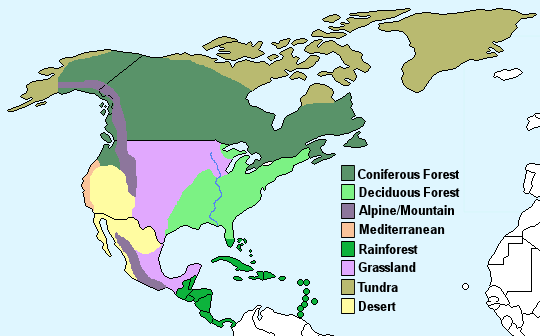
The climate of North America can be broadly divided into eight different climate types:
Deciduous forest – Four distinct seasons with warm summers and cold, wet winters. The trees shed their leaves in autumn.
Coniferous forest – Also known as Taiga, cold and dry with snowy winters and warmer summers.
Mediterranean – Warm to high temperatures with rainfall in the autumn and winter months.
Grassland – Hot summers and cold winters with above average rainfall.
Tundra – This area is characterised by a layer of permafrost (soil that has remained below freezing for at least two years. Winters are very cold, summers are warm and there is little rainfall.
Alpine/mountain – Cold, windy and snowy. It is winter from October to May with temperatures below freezing, while summer is from June to September where the temperature can reach 15°C.
Rainforest – High temperatures and high rainfall throughout the year.
Desert – Warm to high temperatures with very little rainfall.
Countries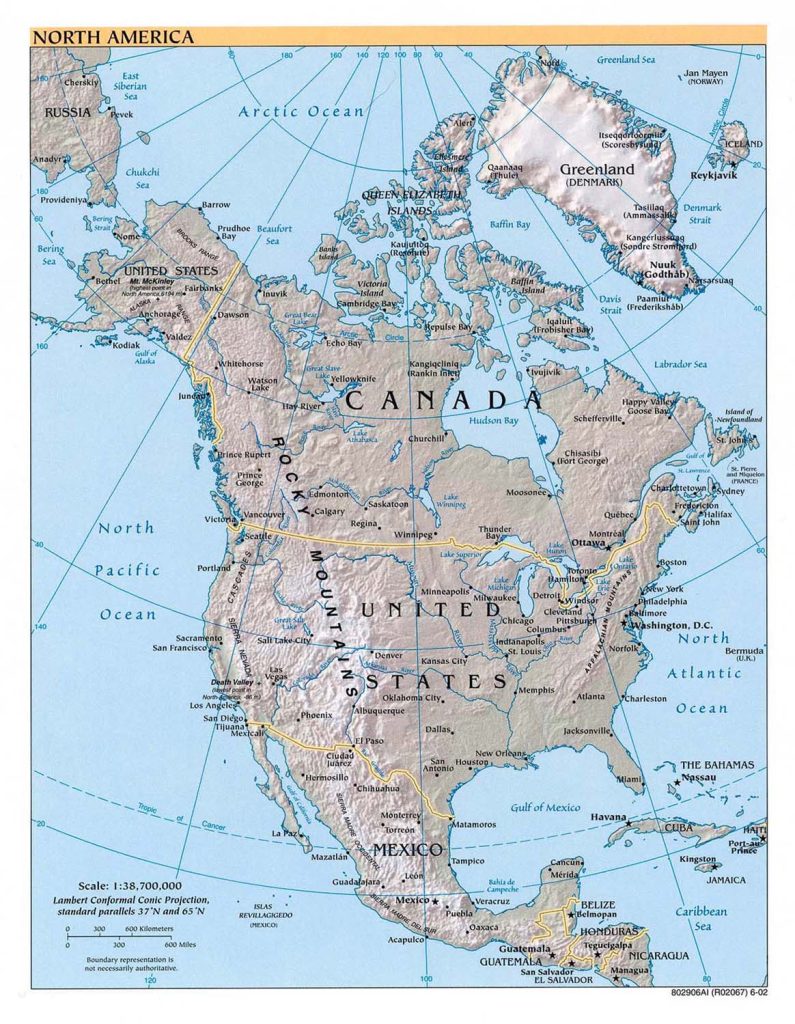
There are 38 countries and Islands in North America.
Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Canada, Cayman Islands, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Greenland, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Martinique, Mexico, Montserrat, Navassa Islands, Netherlands Antilles, Nicaragua, Panama, Puerto Rico, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, United States of America, US Virgin Islands.
Click on the map (right) for a larger image.
Demography
North America is the fourth most populated continent with a total population of around 520,000,000 (2005) about 5.5% of the World’s population. Eastern United States, Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean are the most densely populated areas while Canada, Alaska and Greenland are the least populated areas. The countries with the highest populations (to the nearest million) are:
Unites States – 300 million
Mexico – 106 million
Canada – 33 million
Guatemala – 15 million
Cuba – 11 million
The United States and Canada are the most economically developed countries. The countries of central America and the Caribbean are less economically developed and poorer.
Plant Life

The plant life of North America is characterised according to climatic region.
The deciduous forest region has a wealth of plant life and includes tall and short trees, shrubs, small plants and mosses.
The coniferous forest region contains trees such as pine, fir and spruce. The picture (left) shows a coniferous forest in northern California.
Due to the cold during the winter months, only short grasses and shrubs can survive in the tundra and alpine/mountain regions.
The grassland region is characterised by large open areas of tall or short grass.
Plants found in the Mediterranean region have adapted to the differences in rainfall and temperature between winter and summer and include, palm trees, citrus trees, forest and scrub.
The rainforest areas are jungles of dense, wet forests.
The desert regions are home to those plants that can survive the arid conditions and include varieties of cactii.
Animal Life

North America is home to a range of wild animals including the bobcat , sea otter, racoon and the mountain lion.
Polar bears, wolves and caribou live in the arctic regions of Canada and Greenland.
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). North America. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Continents/north_america.htm. Last accessed Thursday, July 21, 2016
Continents Pages
Africa Antarctica Asia Australasia/Oceania  North America South America
North America South America
