Arctic Hare

Scientific Name – Lepus Articulus
Classification – Lepus
Gender Names – Male – Buck or Jack; Female – Doe; Babies – Leverets
Collective Noun – Drove
Average Length – 55 – 77 cm (19 – 27 in)
Average Weight – 4 – 5.5 kg (9 – 12 lb)
Top Speed – 60km/h (40mph)
Life Expectancy – 4 – 6 years
Mating Season – Spring and Early Summer
Pregnancy – 36-37 days
Special Features – coats turn white in winter for camouflage against predators. They moult during the mating season when their coat turns brown. They can survive in temperatures as low as -36C
Family Unit – live alone or in groups of varying sizes.
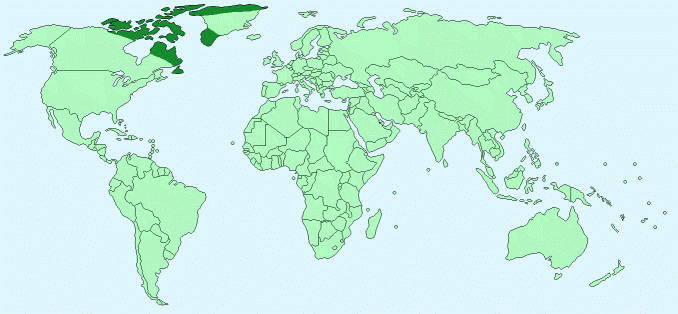
Geographical Distribution – North Pole, Canada, Greenland, Alaska
World Population – Unknown
Conservation Status – Low risk
Natural Habitat – Tundra and Rocky Areas
Diet – Herbivore (vegetarian) – buds, berries, twigs, mosses and woody plants
Predators – Snowy Owls, other birds of prey, wolves, foxes, weasels and polar bears
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Arctic Hare. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Mammals/arctic_hare.htm. Last accessed Monday, July 18, 2016.
Mammals Pages
Features Classification Mammals A – Z
