Africa
Geography
Africa is the World’s second-largest continent – 30,065,000 km² covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s land and 6% of the Earth’s surface .
It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Indian Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the north. The Red Sea and Suez Canal lie to the north-east and separate Africa from Asia.
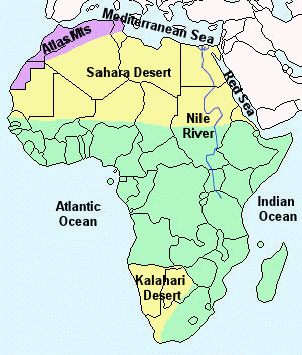
The longest river in the World, The Nile, measuring 6,695 km – flows north ending in a delta that empties into the Mediterranean Sea.
The World’s largest desert, The Sahara, measuring 9,000,000 km², covers much of north Africa. The Kalahari desert in south-west Africa measures 259,000 km².
The Atlas mountain range lies in the north-west of Africa and the highest mountain, Kilimanjaro, 5895 m, is in Tanzania.
Regions & Seasons
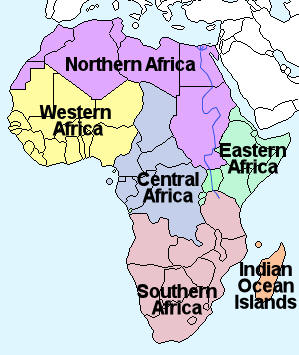
Africa is broadly divided into five regions as shown on the map right.
The seasons are fairly well defined in those regions that lie in the northern and southern hemispheres – the north and south of Africa.
Northern Africa – Spring – March, April, May
– Summer – June, July, August
– Autumn – September, October, November
– Winter – December, January, February
Southern Africa – Spring – August, September, October
– Summer – November, December, January
– Autumn – February, March, April
– Winter – May, June, July
The seasons of western, central and eastern Africa are less easy to define since these regions lie between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn and tend to have a more constant temperature range throughout the year.
Climate
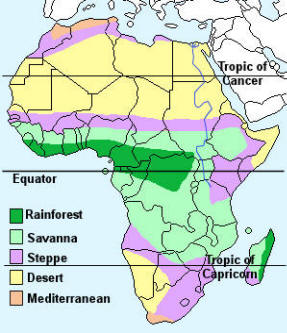
The climate of Africa is governed by its position on the globe and can be broadly divided into five different climate types:
Rainforest – This region is characterised by very high temperatures and high rainfall throughout the year.
Savanna – This region has very high temperatures all year and rain during the summer season only.
Steppe – This region has high temperatures all year and only limited rainfall during the summer season.
Desert – High temperatures throughout the year with very little rainfall.
Mediterranean – Warm to high temperatures with rainfall in the autumn and winter months.
Countries
There are 53 countries in Africa
Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo, Congo (DRC), Cote d’Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome & Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, South Sudan, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, Western Sahara, Zambia, Zimbabwe. Click on the map (right) for a larger image.
Demography
The population of Africa is growing rapidly with a growth rate of approximately 3% per annum.
The total population of Africa is approximately 877,500,000 (2005). The desert regions are the least populated while the most populated areas are in the north, south and around the Gulf of Guinea.
The countries with the highest populations (to the nearest million) are:
Nigeria – 130 million
Egypt – 71 million
Ethiopia – 68 million
Democratic Republic of Congo – 55 million
South Africa – 44 million
Botswana and South Africa are the most economically developed regions while Nigeria is Africa’s largest oil producing region.
About 70% of Africa’s population rely on agriculture for income and times of drought can produce severe hardship. The climate of Africa together with the effects of the Slave Trade, colonisation, international trade and internal wars and conflicts make Africa the World’s poorest continent.
Plant Life

The plant life of Africa is wide and varied and differs according to climatic region.
The desert regions are home to those plants that can survive the arid conditions and include varieties of cypress, olive trees and cactii.
The steppe and savanna regions are characterised by large open areas of tall grass like that shown in the picture (right).
The rainforest areas are jungles of dense, wet forests.
Animal Life

The grassland areas of Africa are home to many well known wild animals including – aardvark, African elephant, antelope, baboon, buffalo, cheetah, giraffe, gnu, hippopotamus, hyena, impala, jackal, leopard, lion, meerkat, mongoose, ostrich, rhinoceros, vulture, wildebeest and zebra.
The rainforest areas are home to a wide variety of insects, birds and animals including – antelope, chimpanzee, gorilla, Mandrill, okapi, hippopotamus and parrots parrots.
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Africa. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Continents/africa.htm. Last accessedThursday, July 21, 2016
Continents Pages
Africa
Antarctica
Asia
Australasia/Oceania
North America
SouthAmerica