Europe
Geography
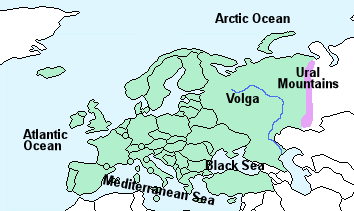
Europe is the World’s second-smallest continent – 10,180,000 km² covering approximately 6.7% of the Earth’s land and 2% of the Earth’s surface .
It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Arctic Ocean to the north and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. The Ural mountains in Russia mark the eastern extreme.
The southern regions are higher and include the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Carpathian mountain ranges.
The longest river in Europe is the Volga (2,850 km) in Russia.
The highest mountain is Elbrus (5,642 m) in Russia.
Regions & Seasons
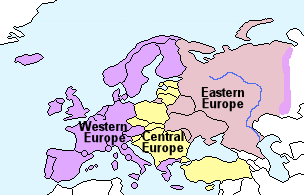
 Europe can be broadly divided into three regions as shown on the map left.
Europe can be broadly divided into three regions as shown on the map left.
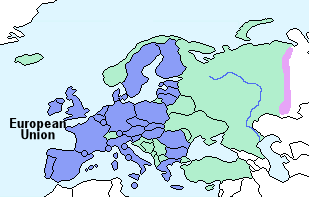
Europe can also be divided according to European Union member states and non-member states as shown on the map right.
Europe lies entirely in the Northern hemisphere and has four distinct seasons
– Spring – March, April, May
– Summer – June, July, August
– Autumn – September, October, November
– Winter – December, January, February
Climate
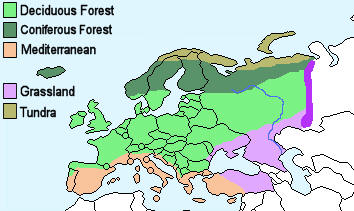
The climate of Europe can be broadly divided into five different climate types:
Deciduous forest – Four distinct seasons with warm summers and cold, wet winters. The trees shed their leaves in autumn.
Coniferous forest – Also known as Taiga, cold and dry with snowy winters and warmer summers.
Mediterranean – Warm to high temperatures with rainfall in the autumn and winter months.
Grassland – Hot summers and cold winters with above average rainfall.
Tundra – This area is characterised by a layer of permafrost (soil that has remained below freezing for at least two years. Winters are very cold, summers are warm and there is little rainfall.
Countries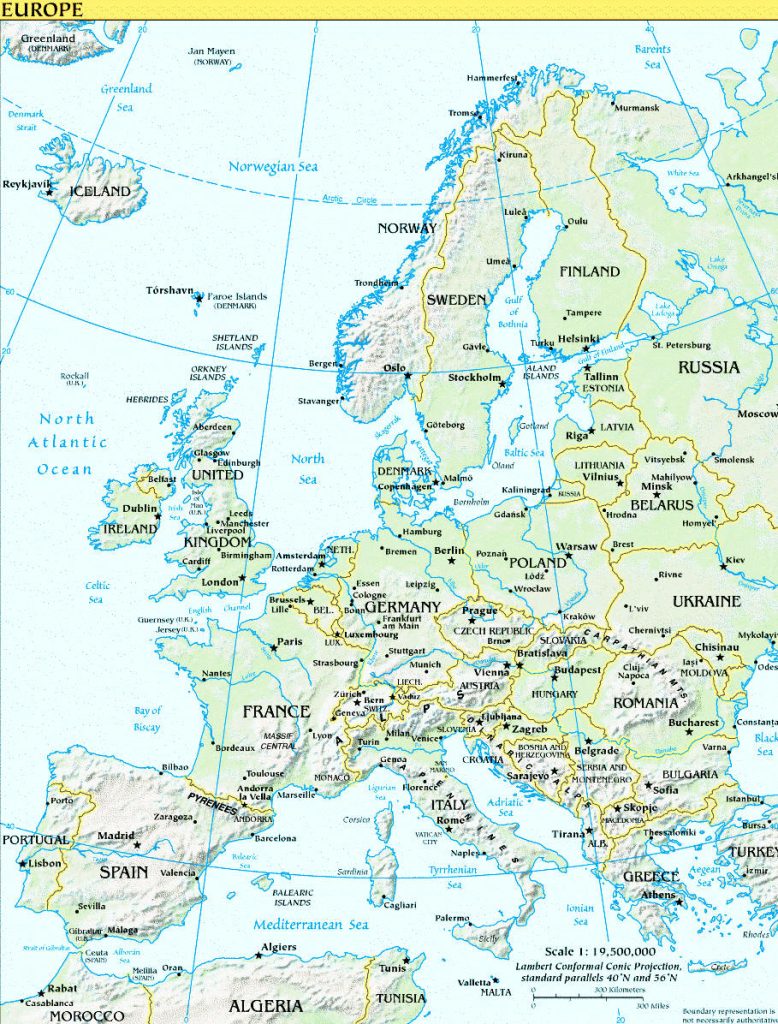
There are 47 countries in Europe including Turkey and Russia which lie in both Europe and Asia.
Albania, Andorra, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, San Marino, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, Ukraine, United Kingdom, Vatican City.
Click on the map (right) for a larger image.
Demography
Europe is the third most populated continent with a total population of around 729,000,000 (2006) about 11% of the World’s population. Southern England, western Germany, the Netherlands and northern Italy are the most populated areas while Iceland, northern Scandinavia and northern Russia are the least populated.
The countries with the highest populations (to the nearest million) are:
Russia – 106 million
Germany – 83 million
United Kingdom – 60 million
France – 60 million
Italy – 60 million
Europe has the largest economy of the world with Germany and the United Kingdom being the most economically developed countries.
The countries of central and eastern Europe are the least economically developed and are poorer in relation to the western countries.
Plant Life

The plant life of Europe is characterised according to climatic region.
The deciduous forest region has a wealth of plant life and includes tall and short trees, shrubs, small plants and mosses. The picture (left) shows a deciduous forest region of Hungary.
The coniferous forest region contains trees such as pine, fir and spruce.
Due to the cold during the winter months, only short grasses and shrubs can survive in the tundra region.
The grassland region is characterised by large open areas of tall or short grass.
Plants found in the Mediterranean region have adapted to the differences in rainfall and temperature between winter and summer and include, palm trees, citrus trees, forest and scrub.
Animal Life

Due to the density of population in Europe there are few areas of natural habitat remaining and many indigenous animals are now extinct or in danger of extinction.
Brown bears and wolves can be found in the northern coniferous forest regions.
Deer, foxes, hedgehogs, snakes and wild cats can be found in the deciduous forest regions.
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Europe. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Continents/europe.htm. Last accessedThursday, July 21, 2016
Continents Pages
Africa Antarctica Asia Australasia/Oceania Europe North America South America
