African Elephant

Scientific Name – Loxodonta africana
Classification – Proboscidea (Ungulate)
Gender Names – Male – Bull, Female – Cow, Baby – Calf
Collective Noun – Herd
Average Height – Males – 3 – 4 metres; Females – 2 – 3 metres
Average Length – 6 – 7.5 metres
Average Weight – Males – 5,000 – 6,000 kg; Females – 2,000 – 3,500 kg
Top Speed – 6km/h (4mph) normally; up to 40km/h (25 mph) stampede
Life Expectancy – 50 – 70 years in the wild, 80+ years in captivity
Mating Season – No specific time
Pregnancy – 22 months
Special Features – Long trunks used to pick up things and suck up water, large ivory tusks used for digging roots and stripping bark from trees, large flapping ears used to keep cool.
Family Unit – Older matriarch, female offspring and young; males leave the females at 16 years and either join other males or remain solitary. They visit female groups for mating.
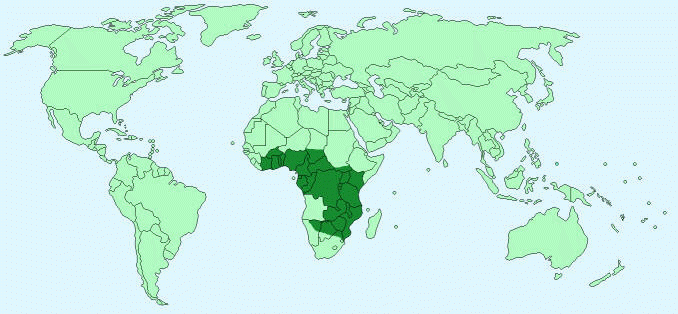
Geographical Distribution – Central and Southern Africa
World Population – 500,000 – 700,000 (approx)
Conservation Status – Vulnerable
Natural Habitat – Savanna plains, African rainforest
Diet – Herbivore (vegetarian) – roots, grasses, fruit, and bark
Predators – Adults – Man; Babies – Man, lions, crocodiles, hyenas, cheetahs,
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). African Elephant. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Mammals/african_elephant.htm. Last accessed Monday, July 18, 2016
Mammals Pages
Features Classification Mammals A – Z
