African Lion
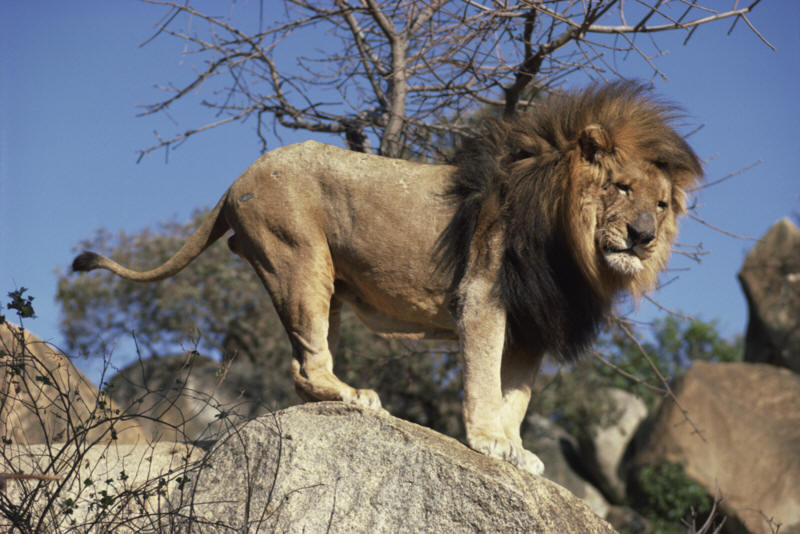

Scientific Name – Panthera Leo
Classification – Carnivore
Gender Names – Male – Lion; Female – Lioness; Baby – Cub
Collective Noun – Pride
Average Height – 1.2 m (4 feet)
Average Length – 1.5 – 2.4 m (5 – 8 feet)
Average Weight – Males – 150-227 kg (330-550Ibs) Females – 120-190 kg (260-400Ibs)
Top Speed – 80 km/h (50 mph)
Life Expectancy – 13-18 years in wild; 25-30 years in captivity
Mating Season – No specific time
Pregnancy – 100-120 days.
Special Features – Male lions have a mane which darkens with age, eventually turning dark brown.
Family Unit – Lions live in groups called a pride consisting of female lions and their cubs. Sometimes a male will join a pride but others prefer to remain solitary. Female lions do all the hunting and are the food providers while any males will defend the group.
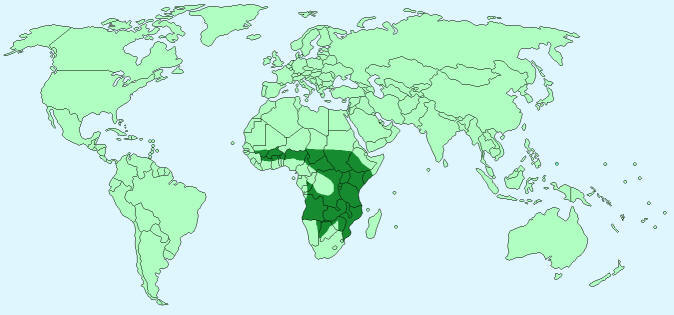
Geographical Distribution – Sub-Saharan Africa (Central and Southern Africa)
World Population – 16,500 – 47,000
Conservation Status – Vulnerable
Natural Habitat – Grassy plains, Savannas, Semi-deserts
Diet – Carnivore (meat eater) – giraffe, buffalo, antelope, zebra, wildebeest, wild hogs
Predators – Adults – man; Babies – rival male lions, other predators.
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). African Lion. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Mammals/african_lion.htm. Last accessed Monday, July 18, 2016
Mammals Pages
Features Classification Mammals A – Z
