Dingo

Scientific Name – canis lupus dingo
Classification – Carnivore
Gender Names – Male – dog; Female – bitch; Baby – pup
Collective Noun – packs
Average Height – 52 – 60 cm (20 – 24in)
Average Length – 117 – 124cm (42 – 48in)
Average Weight – 10 – 15kg (22 – 33lbs)
Top Speed – 65 km/h (40 mph)
Life Expectancy – 6 – 14yrs
Mating Season – No particular time of year
Pregnancy – 63 days
Special Features – Dingoes can turn their heads almost 360 degrees to track other animals, such as birds in flight. Dingoes do not bark but they do howl, snort and purr.
Family Unit – They form small packs in which the dominant pair become the breeders. The entire pack helps care for the young. They also hunt together.
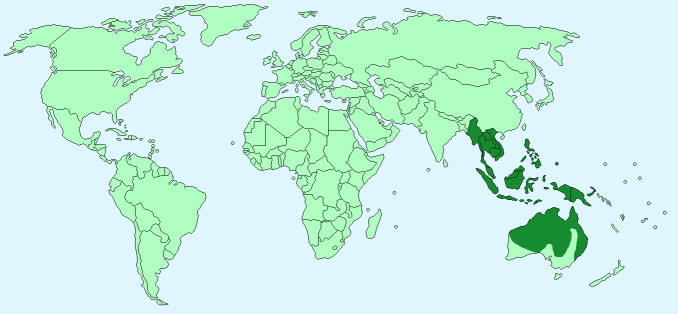 Geographical Distribution – Australia and Southeast Asia
Geographical Distribution – Australia and Southeast Asia
World Population – Unknown
Conservation Status – vulnerable
Natural Habitat – grassland, forest
Diet – geese, wallabies, kangaroos, lizards, rabbits, mice, rats, insects and water buffalo
Predators – humans, wild dogs
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Dingo. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Mammals/dingo.htm. Last accessedMonday, July 18, 2016
Mammals Pages
Features Classification Mammals A – Z
