Giant Panda
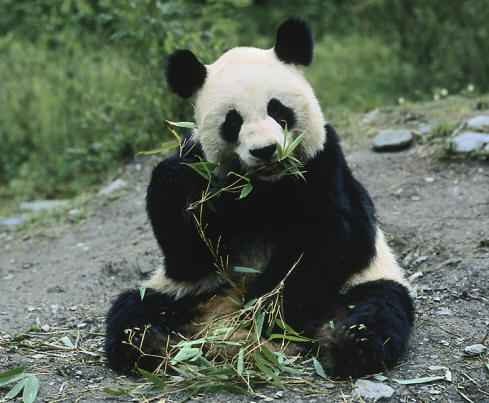

Scientific Name – Ailuropoda melanoleuca
Classification – Ursidae
Gender Names – male – boar, he-bear; female – sow, she-bear; baby – cub
Collective Noun – Sleuth
Average Height – Fully grown they reach the height of 1.2 – 1.8 metres (4 – 6 feet)
Average Weight – An adult weighs about 125 kg (280 pounds)
Top Speed – 32 km/h (20mph)
Life Expectancy – 15 – 20 years in the wild, up to 35 years in captivity
Mating Season – Between March and May
Pregnancy – from 95 to 160 days.
Special Features – Able to climb, diet mainly bamboo shoots
Family Unit – Giant pandas are solitary and most live alone only meeting other pandas at breeding times. Sometimes small groups will share a large feeding area.
 Geographical Distribution – Native to the mountainous regions of central and southern China
Geographical Distribution – Native to the mountainous regions of central and southern China
World Population – 1000 – 1500
Conservation Status – Endangered
Natural Habitat – cool, wet, cloudy mountain forest lands where bamboo grows.
Diet – herbivorous, almost exclusively bamboo.
Predators – adults have few predators besides man but cubs are a very small and may be vulnerable to leopards.
Harvard Reference for this page:
Heather Y Wheeler. (2015). Giant Panda. Available: https://www.naturalhistoryonthenet.com/Mammals/giant_panda.htm. Last accessed Monday, July 18, 2016
Mammals Pages
Features
Classification
Mammals A – Z
